Challenges of Interoperability in Healthcare and How To Overcome Them
An average clinic holds up to 12% of duplicated medical records. Moreover, up to 14% of records imply incorrect patient data, which is one of the EHR interoperability challenges.
According to the report prepared by EHRIntelligence, 88% of hospitals can exchange clinical data electronically. Other organizations can only share information at a basic level or cannot exchange medical data because of the challenges they cannot overcome.
In the post, you will discover the foremost challenges of interoperability in healthcare and the healthcare interoperability adoption barriers.
WHAT IS INTEROPERABILITY IN HEALTHCARE?
Interoperability in healthcare describes the ability of different medical care providers to exchange data with the unification approach in mind. Also, it enables medical institutions to build systems that consist of various digital solutions from disparate vendors.
How Does Interoperability Work?
In a nutshell, interoperability needs medical organizations to use standardized data formats and exchange protocols to share data between different systems. Hence, systems that use different technologies can send and receive messages that contain diverse information and interpret it error-free.
The most popular data interoperability standards used by healthcare organizations are:
- Health Level 7 (HL7) — A popular data interoperability standard that helps exchange medical data using standardized messages and documents.
- Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) — A clinical data unification standard that helps send and receive medical imaging information by different systems.
- openEHR — The standard defines rules on storing, sending, and fetching medical data to enable standardization.
Read also:
What are the Examples of Interoperability?
Let’s check the example of interoperability in healthcare by examining how a doctor uses diverse systems to request radiology results in a few clicks.
The use scenario implies the following actions:
- A doctor submits a lab test results request using an electronic health record (EHR) system.
- The EHR system sends a request to an HL7 integration engine.
- The HL7 integration engine transforms the request into a standardized message and sends it to a radiology information system (RIS).
- The RIS process the request and send radiology results back.
- The HL7 integration engine transforms the message into a standardized message and sends it to the EHR system.
- The doctor reviews radiology results transferred to the EHR system.
Build fully-compatible solution
Another example of interoperability application in healthcare is the submission of a prescription order.
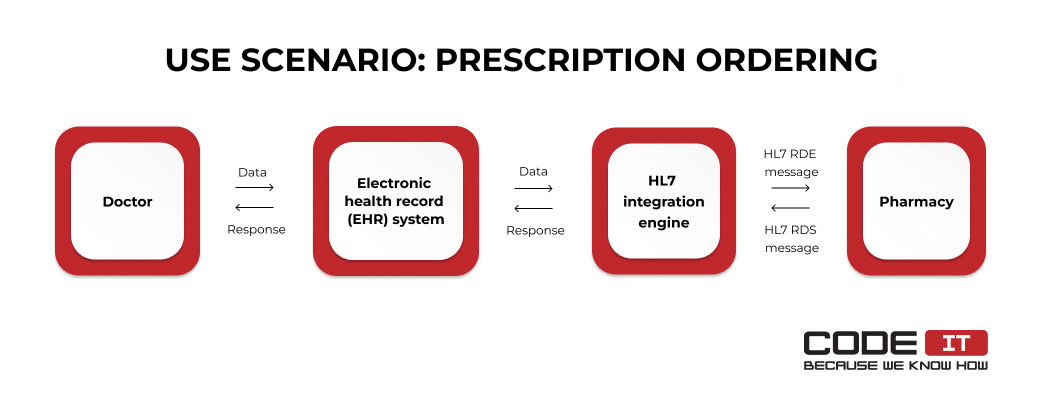
Let’s check all the steps of the process in more detail.
- A doctor submits a request using an EHR.
- The request is passed to an HL7 integration engine and forwarded to a pharmacy.
- The pharmacy processes the request and sends a confirmation message to the EHR through the integration engine.
- Once the requested medicine is dispensed, the status update message is sent to the EHR automatically.
What are the Benefits of Interoperability?
Medical data interoperability standards are widely adopted in healthcare because of their many benefits, including the following.
- Integration of different software. The use of standardized messages enables medical organizations to combine various systems that use different technologies.
- Improved collaboration. The standardized exchange of medical data helps create collaborative environments.
- Seamless data sharing. Hospitals can share medical data between different departments. Also, they can send information about patients to other clinics in a few clicks.
- Reduced number of errors. Thanks to automated message composition, data validation, and response checking, the adoption of interoperability helps reduce the number of errors in daily operations.
- Regulatory compliance. Many regulatory organizations obligate medical institutions to adopt interoperability standards to exchange medical data electronically.
- Improved patient care. The standardized data exchange between medical providers eliminates the need for patients to bring their lab test results or re-submit all the information many times.
- Enhanced performance. Collaborative environments and automation help medical staff optimize their work processes.
EHR INTEROPERABILITY CHALLENGES IN HEALTHCARE
Statistics say that roughly 32% of patients experienced problems caused by a lack of interoperability in healthcare. Let’s learn more about the challenges of interoperability in healthcare faced by medical providers.
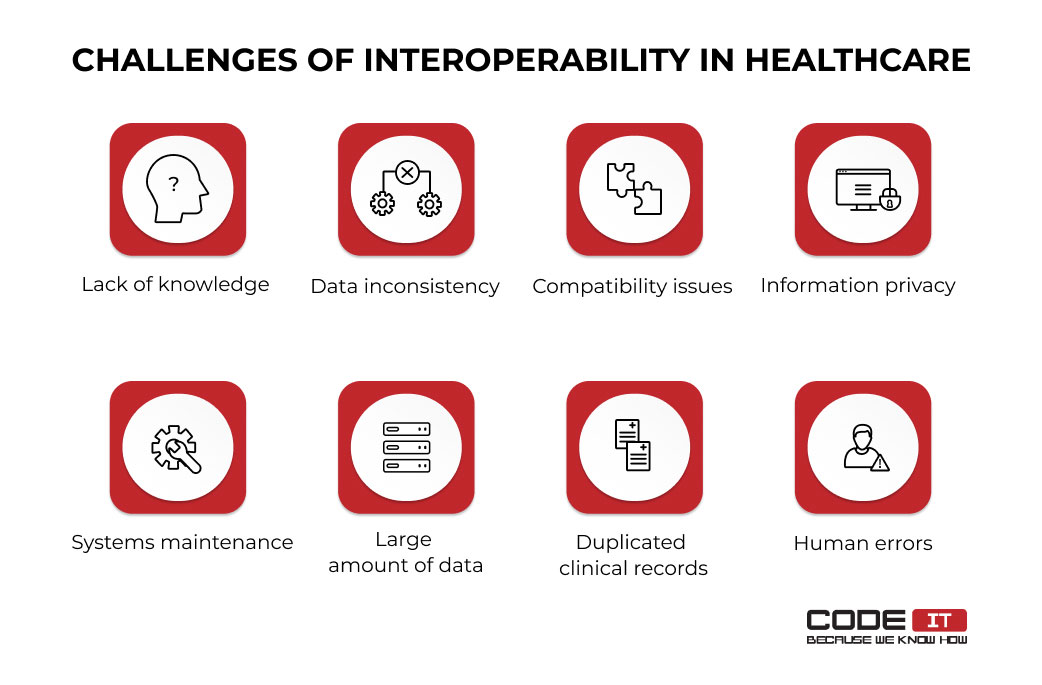
Lack of Knowledge
Interoperability adoption is related to the integration of new systems and technologies. Medical staff may need higher digital literacy. Hence, additional staff training may be required to implement new software solutions in a clinic.
Data Inconsistency
The need for centralized databases to store medical information leads to data consistency across the industry. Roughly 11% of medical records imply incomplete or erroneous information about patients because clinical data is usually fetched from various sources containing different information about a patient.
Compatibility Issues
Interoperability standards in healthcare may not be compatible with each other. Therefore, medical organizations that use various systems may experience serious challenges of interoperability in healthcare.
Moreover, one standard may have different versions that are not backward compatible. For example, the top versions of the HL7 standards (V2, V3, CDA, and FHIR) are not fully compatible. Feel free to read about the compatibility of HL7 standards in our article.
Read also:
Information Privacy
HIPAA regulations need clinics to store and process personal information wisely to address patient safety concerns. Healthcare providers must develop secure systems to withstand the majority of interoperability and security issues. Also, they need to create data backups to prevent the loss of information.
Systems Maintenance
Systems that help store and share data and storage should be constantly maintained and upgraded. Database engineers should be involved in monitoring the use of resources and upgrading the infrastructure of a hospital upon demand.
Also, it’s necessary to involve a network engineer who will establish a new network infrastructure and maintain it, especially when enabling the Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare. IoT-driven systems imply a lot of sensors and devices that collect, process, and transmit a lot of data in real-time.
Large Amounts of Data
Clinical software needs to process a lot of data fetched from other systems or entered by medical staff. The lack of computing power, insufficient bandwidth, or data storage shortage may cause the failure of a system.
Duplicated Clinical Records
On average, every 10th medical record is a duplicate. Since there is no universal patient ID, diverse medical providers can create disparate records about patients and share them with other hospitals.
Human Errors
Even though most systems validate entered data, there is a high chance of entering misleading information. Also, the personnel of a clinic may not follow provided instructions directly or miss crucial data submission or retrieval steps in their workflows.
We are ready to help you adopt interoperability standards!
BARRIERS TO INTEROPERABILITY IMPLEMENTATION
While implementing standardized data exchange interfaces, organizations need to overcome many challenges of interoperability in healthcare.
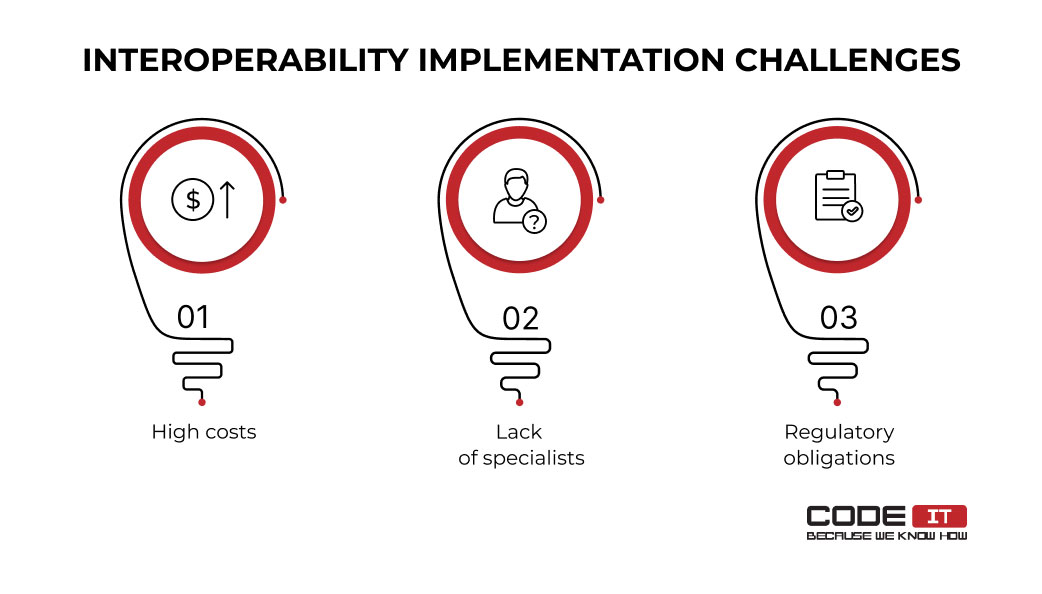
The top three interoperability issues during the implementation process are as follows.
High Costs
The adoption of interoperability needs medical institutions to develop Health Information Exchange (HIE) networks, upgrade their infrastructures, and install new software. They need to involve a lot of specialists and invest in new hardware, which causes high expenses. Furthermore, some interoperability standards vendors charge installation and support fees.
Lack of Specialists
When implementing a clinical data interoperability system, clinics must involve experts with defined technical expertise and certification. A clinic may be required to scout and hire the following IT experts:
- Data engineer
- Database engineer
- Software engineer
- Cybersecurity specialist
- Network engineer
Hire developers with HL7 expertise
According to Forbes, there is a global shortage of data experts and engineers. In addition, involved experts should hold specific certifications. For example, HL7 integration specialists need to hold the corresponding certification.
Let’s check the average salaries and shortage rate of the specialists that may be involved in the implementation of interoperability standards in healthcare.
The shortage rate indicates the global deficit of IT professionals specified in the report.
| Role | Average Annual Salary |
Shortage Rate |
| Data Engineer | $115,665 | 40% |
| Database Engineer | $172,858 | 31% |
| Software Engineer | $107,428 | 28% |
| Cybersecurity Specialist | $90,728 | 43% |
| Network Engineer | $88,889 | 11% |
Regulatory Obligations
Clinics need to comply with patient data privacy and security requirements when implementing new interoperability standards.
The foremost regulatory obligations are:
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH Act)
- Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA)
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) interoperability requirements
Medical organizations need to follow defined frameworks, use specific technologies, and compromise on some features to comply with all the EHR interoperability requirements.
Read also:
HOW TO IMPROVE EHR INTEROPERABILITY
The improvement of clinical data interoperability can be achieved in different ways. Let’s check the most-effective ways to improve EHR interoperability.
Develop Cloud-Based Systems
The implication of cloud-based systems enables healthcare providers to store patient data efficiently and securely. Data stored in a cloud can be easily retrieved by different software. Storage space and computing power of cloud-based servers can be easily adjusted to spend resources wisely.
Use an Integration Engine
The use of an integration engine is the alternative to establishing point-to-point connections between two systems. It foresees the opportunity to connect a lot of digital solutions from different vendors into one system.
An integration engine acts like a hub that routes messages. Also, it can transform and validate processed data.
Standardize Data
Using inconsistent data is one of the foremost challenges of interoperability in healthcare. It’s advisable to develop rules on composing medical data and follow them when creating new records and updating the existing ones.
Also, you can implement semantic interoperability to empower data standardization by using defined terminologies when composing new medical records.
Test and Monitor All Processes
The continuous monitoring of the performance, data flow, errors, and other crucial metrics can help identify bottlenecks and unforeseen EHR interoperability issues. Also, it’s advisable to test all the software in your organization to ensure that messages are composed and shared error-free to detect any possible data interoperability issues in healthcare in the early stages.
UNIFIED MEDICAL SOLUTIONS — CODEIT EXPERTISE
Our team of eight experts has developed an innovative system for rapid medical data analysis. We’ve incorporated the best healthcare data interoperability practices to enable seamless information exchange.
Problem
The client experienced issues with fast and efficient medical data transfer to labs for further analysis. Hence, he has requested our team to build a new solution for automatic processes and enabling medical data interoperability.
Solution
The business analyst interviewed stakeholders and thoroughly analyzed the provided requirements. The solution architect has selected the best tech stack and solution creation plan.
The team of software engineers dedicated to the project has developed a mobile application. The Flutter-based works on different platforms using a one codebase. It helps speed up the medical testing process. Using the application, medical staff can quickly take photos, send them to labs, and receive easy-to-understand documents.
Read about the features developed to discover how the app works in more detail.
Case study:
TO RECAP
The adoption of interoperability provides a lot of benefits to medical organizations. Statistics say that 92% of doctors are confident that medical data interoperability helps improve the patient experience.
To enable bata standardization, clinics need to tackle a lot of issues. The foremost challenges of interoperability in healthcare are as follows.
- Lack of knowledge
- Data inconsistency
- Compatibility issues
- Information privacy
- Systems maintenance
- Large amounts of data
- Duplicated clinical records
- Human errors
Moreover, clinics may face barriers when implementing interoperability, including the following:
- High costs
- Shortage of specialists
- Regulatory obligations
Hire certified IT specialists to enable interoperability
The data standardization approach enables clinics to share unified medical data between different hospitals’ EHRs.
For instance, with the help of medical data interoperability, a doctor can submit a transfer request and send a patient’s medical records to another hospital in a few clicks.
Medical data interoperability enables clinics to connect different systems that use diverse technologies.
Using standardized messages, a lab can send test results to an EHR automatically once they are completed. Hence, doctors can access and check lab test results without the need to request them manually.
The process of integrating clinical data interoperability standards implies the following steps:
- Existing environments analysis
- Standards compatibility definition
- Integration option selection
- Vendor selection
- Integration project initiation
- Testing and validation
The foremost EHR interoperability issues are the following:
- Lack of knowledge
- Data inconsistency
- Compatibility issues
- Information privacy
- Systems maintenance
- Large amounts of data
- Duplicated clinical records
- Human errors
The top seven benefits of EHR interoperability are:
- Integration of different software
- Improved collaboration
- Seamless data sharing
- Reduced number of errors
- Regulatory compliance
- Improved patient care
- Enhanced performance
The top ways to improve interoperability in healthcare are:
- Use cloud-based infrastructure
- Utilize integration engines
- Standardize data
- Test and monitor all the processes
The top three barriers to adopting interoperability in healthcare are as follows.
- High costs
- Lack of specialists
- Regulatory obligations
